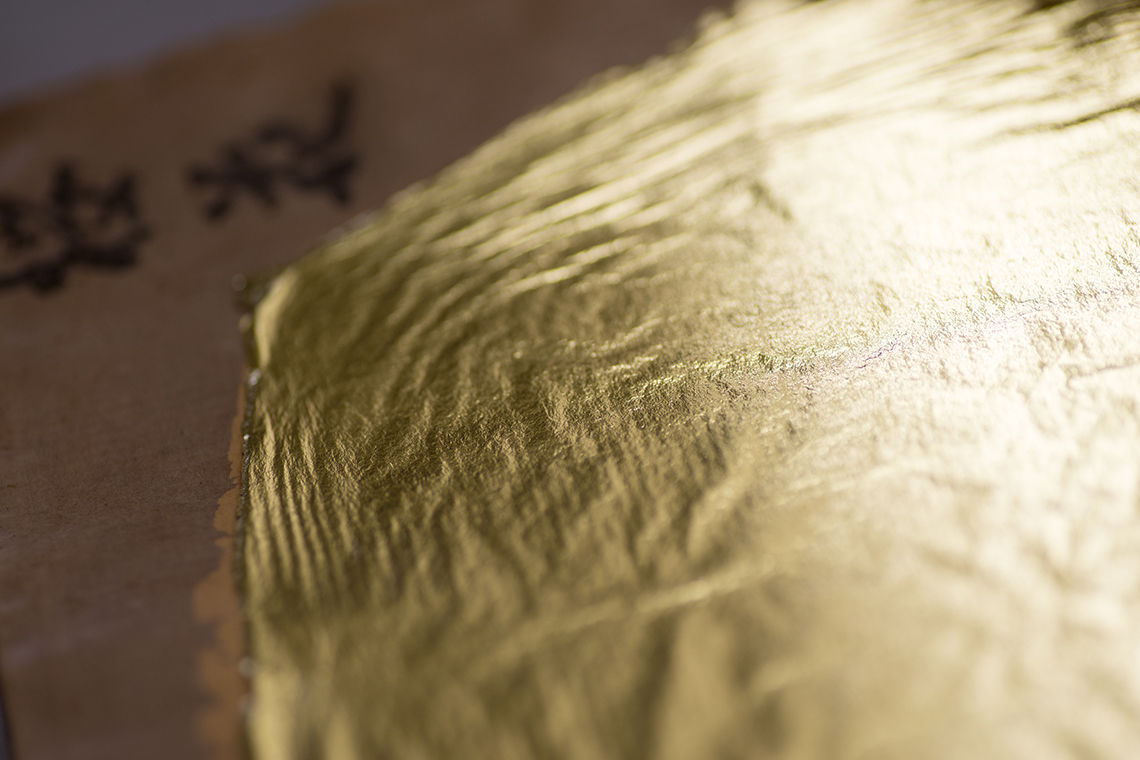
Entsuke gold leaf production processes
Entsuke gold leaf production processes
The traditional entsuke gold leaf production method consists of three processes.
In order to create thin, soft gold leaf, each process, which consists of experienced craftsmen’s techniques, must be integrated.
In order to create thin, soft gold leaf, each process, which consists of experienced craftsmen’s techniques, must be integrated.
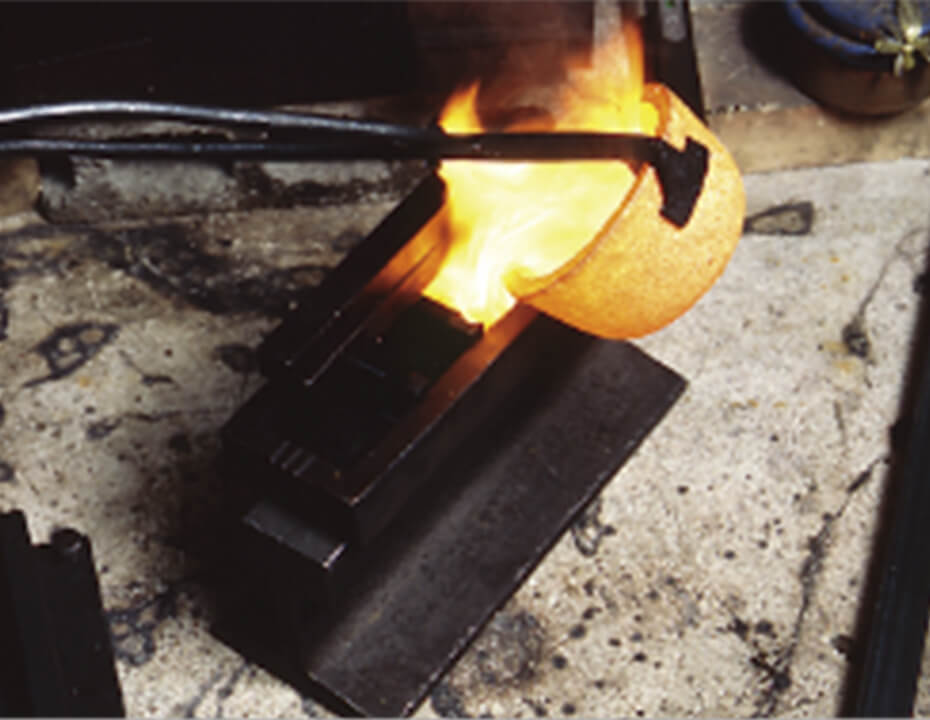

Zumi (gold foil) production process
Gold alloy is made and beaten to a thickness of one micron by zumi craftsmen (zumiya).
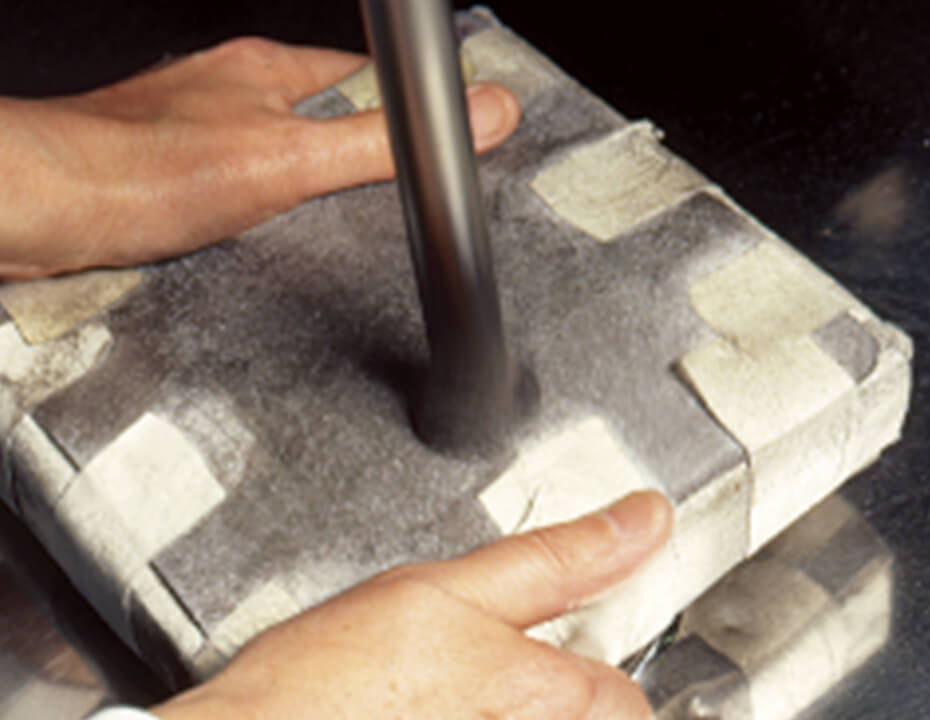

Haku (gold leaf) production process
The gold leaf is further beaten to a thickness of 0.1 micron by haku beating craftsmen (hakuya).
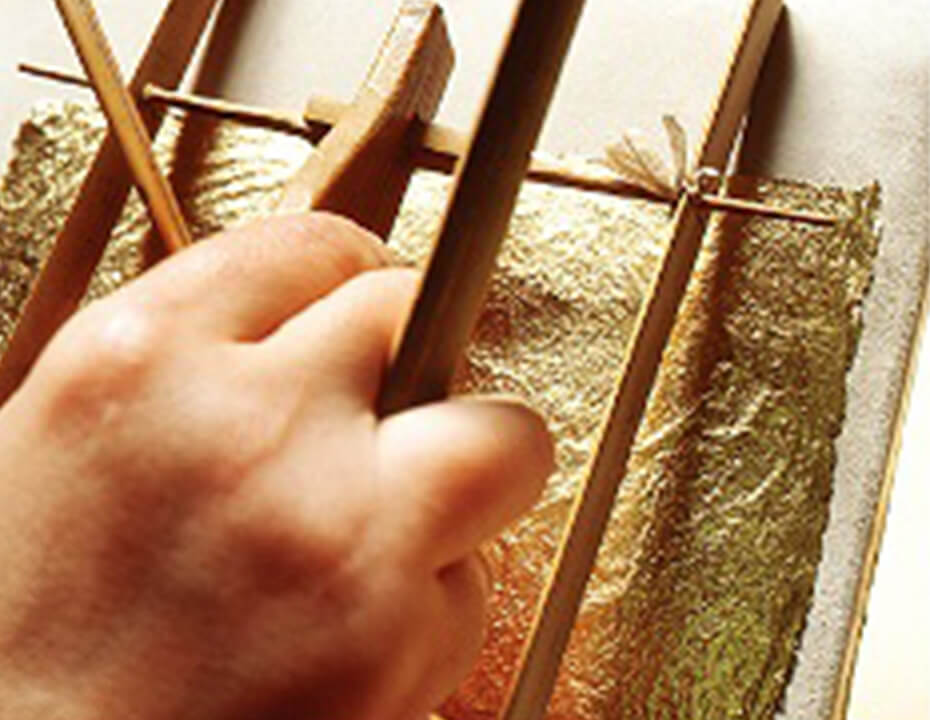

Booking (finish)
Sheets of 0.1 micron gold leaf are trimmed into squares one by one by gold booking craftsmen.
Zumi gold beating processThickness: ~1 micron
Melting and casting
Gold, silver and copper are melted at 1,300ºC to make alloy. The alloy compositions differ depending on the gold leaf type.

Nobegane : rolling and cutting
The gold alloy is extended and formed into a belt shape using a rolling mill. The extended gold alloy is referred to as nobegane.
Gold beating paper preparation
Zumi gold beating
Koppe : first beating
The extended gold alloy (nobegane) is cut into 5cm×5cm pieces. Each piece is inserted between sheets of beating paper and extended using a beating machine into 13cm×13cm sheets, which are referred to as koppe.
Aragane : second beating
The koppe is inserted between new sheets of gold beating paper and further extended into 18cm×18cm sheets, which are referred to as aragane.
Koju : third beating
Each aragane is cut into four sheets, inserted between sheets of small beating paper (koju) and extended to match the paper size.
Oju : fourth beating
The gold foil beaten in the koju process is inserted between sheets of large beating paper (oju) and extended to match the paper size.
Keshouchi : finishing
The gold foil beaten in the Oju process is inserted between sheets of kraft paper and beaten lightly to create a matte surface.
Trimming and packing
The gold foil is trimmed with a knife to 20cm×20cm. It is referred to as uwazumi, or shiage-zumi (finished zumi).
Final gold leaf beating (haku)
Thickness: decreased from 1 micron to 0.1 micron
Zumi cutting
The 20cm×20cm uwazumi gold foil is cut into nine to twelve pieces, using chopsticks.
Bundling
The uwazumi pieces are inserted between sheets of gold beating paper.

Beating
Around 1,800 sheets of paper with uwazumi leaf are bundled together in leather cloth and fastened with a leather belt, then beaten until the uwazumi pieces are extended into 10cm×10cm sheets, which are referred to as koma.
Rebundling
The leaf sheets beaten in the koma process are inserted between sheets of beating paper one by one.
Beating
The koma gold leaf sheets and paper are bundled in leather cloth and fastened with a leather belt, then beaten until the gold leaf is a thickness of 0.1 micron.*The bundles are beaten using a machine for 10 to 15 minutes and then opened to cool down. This process is repeated several times.

Grading
Each gold leaf sheet is removed from the gold beating paper, inspected, sorted according to quality, and inserted into a leaf ledger one by one.*The beating paper is reused for beating after the remaining gold particles are removed.
Booking (finish)
Trimming and booking
The gold leaf is transferred from the leaf ledger onto a leather base using bamboo pincers, and trimmed with a bamboo frame. Each gold leaf sheet is layered alternately with mitsumata paper, and 100 sheets are bundled together with thread.

*Entsuke (with a margin) gold leaf was named due to its finished state, in which the paper is larger than the gold leaf, creating a margin.
*It takes about one week to extend zumi leaf into the final gold leaf, although the period differs depending on the craftsmen and working conditions.
Gold beating paper preparation
Gold beating paper preparation is the most important work for craftsmen in the entsuke gold leaf production processes. The quality of the beating paper determines the quality of the gold leaf. This is why gold leaf craftsmen are only regarded as fully capable after they have acquired this technique.
In order to make gold beating paper, traditional handmade Japanese paper made from ganpi plant fibers is soaked in water, straw ash lye, persimmon tannin and egg white*1 and beaten using a machine. This process is repeated for half a year.
The used paper, which has lost strength, is treated and reused several times.*2
In order to make gold beating paper, traditional handmade Japanese paper made from ganpi plant fibers is soaked in water, straw ash lye, persimmon tannin and egg white*1 and beaten using a machine. This process is repeated for half a year.
The used paper, which has lost strength, is treated and reused several times.*2
*1: Depending on the craftsmen, egg white may not be used.
*2: After being used many times and having lost its strength, the paper is used as furuya paper (facial blotting paper).






